Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Question Answer – PDF
The post Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Question Answer – PDF contains important questions from chapter Matter in Our Surroundings of class 9 science. PDF is available at the end of this post.
Que 1. Which of the following are matter? Chair, air, love, smell, hate, almonds, thought, cold, cold drink, the smell of perfume.
Ans 1. Chair, air, almond, cold-drinks
Que 2. What happens to the sugar when it dissolves in water? Where does the sugar go? What information do you get about the nature of matter from the dissolution of sugar in water?
Ans 2. (a) When sugar dissolves in water, its tiny particles break off from the solid sugar crystals.
(b) The sugar particles go into the spaces between the particles of water and mix with them (to form a sugar solution).
(c) The dissolution of sugar in the water tells us that
i) The matter (here sugar and water) is made up of small particles.
ii) The particles of matter (here water) have spaces between them.
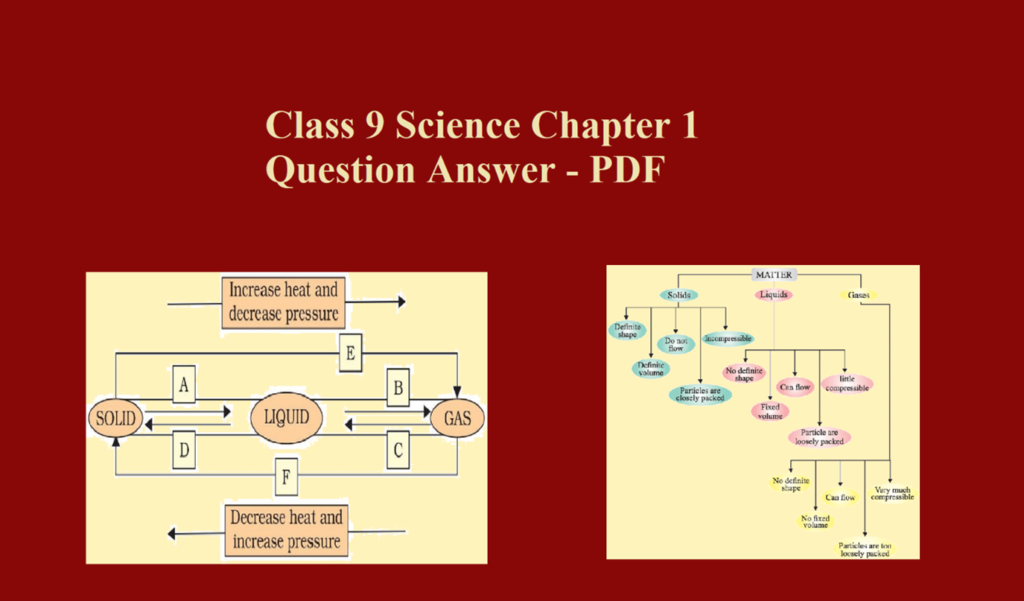
Que 3. Name the three states of water.
Ans 3. Ice (solid), water (liquid), steam (gas)
Que 4. Name the physical state of matter
(a) Which can be easily compressed
(b) Which is most rigid
(c) Which can flow but cannot fill the vessel completely.
Ans 4. (a) Gas
(b) Solid
(c) Liquid
Que 5. Find the rate of diffusion in various state of matter that is solid, liquid and gas.
Ans 5. Solid < Liquid < Gases
Que 6. (a) Give two reasons for saying that wood is solid.
(b) ‘A substance has a definite volume but no definite shape. State whether this substance is a solid, a liquid or a gas.
(c) Name the physical state of matter which can be easily compressed.
(d) ‘A substance has a definite shape as well as a definite volume’. Which physical state is represented by this statement?
(e) A substance has neither a fixed shape nor a fixed volume. State whether it is a solid, a liquid or a gas.
(f) Give two reasons to justify that:
i) Water is a liquid at room temp.
ii) An iron almirah is solid.
Ans 6. a) Wood has (i) fixed shape, and (ii) fixed volume
b) Liquid
c) Gas
d) Solid
e) Gas
f) i) Fixed volume but no fixed shape
ii) Fixed shape and fixed volume.
Que 7. What is the common name of solid carbon dioxide?
Ans 7. Dry ice.
Que 8. Define melting process
Ans 8. The process in which a solid substance changes into a liquid on heating is called melting.
Que 9. What is the latent heat of fusion of ice
Ans 9. 3.34 × 105 j/kg
Que 10. Why the temperature of melting ice does not rise even though heat is being supplied continuously?
Ans 10. Ice is a solid substance, so the particles of ice attract one another with strong forces. These forces of attraction hold the particles closely packed in solid ice. The heat which we supply to the ice during melting is all used up to overcome the forces of attraction between ice particles so that they become somewhat loose and form liquid water. This heat does not increase the kinetic energy of particles and hence no rise in temperature takes place during the melting of ice. But when all the ice has melted to form water, further heating increases the kinetic energy of water particles due to which the temperature of water starts rising sharply.
Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Question Answer
Que 11. What happens when you pour acetone on your palm?
Ans 11. Acetone has a very low boiling point. It instantly vaporises into vapours. The evaporation of the liquid is an endothermic process. Thus, acetone takes up heat from the hand. Therefore, the palm immediately turns cold or even numb.
Que 12. When 50 g of sugar is dissolved in 100 mL of water, there is no increase in volume. What characteristic of matter is illustrated by this observation?
Ans 12. This observation indicates that particles of water have spaces between them into which sugar particles fit.
Que 13. Convert the following temperature to a Celsius scale:
i) The temperature is 300 K.
ii) The temperature is 573 K
Ans 13. (i) When we use: K = 273 + ⁰C
⁰C = K – 273
= 300 – 273
= 27⁰C
(ii). When we use: K = 273 + ⁰C:
⁰C = 573 – 273
= 300 ⁰C
Que 14. What happens to the rate of diffusion if the temperature is increased?
Ans 14. With increased temperature, the rate of diffusion also increases as the particles gain energy and move fast.
Que 15. Sponge, though compressible, is a solid?
Ans 15. A sponge has minute holes in which air is trapped. When we press it, the air is expelled out and we are able to compress it. On releasing pressure, it again regains its shape. So, it is classified as a solid.
Que 16. What is evaporation? What are various factors that affect the rate of evaporation?
Ans 16. Evaporation is a kind of vaporisation that generally occurs on a liquid surface and involves the transition of the liquid into a vapour state at any temperature below its boiling point. The evaporation of the liquid is affected by the following factors.
♦ Temperature
♦ Humidity
♦ Surface area
♦ Wind speed
Que 17. Name the state of matter in which:
(i) Layers of particles can slip and slide over one another easily.
(ii) Particles just move around randomly because of a very weak force of attraction.
Ans 17. (i) Liquid state,
(ii) Gaseous state
Que 18. Liquids generally have a lower density as compared to solids. But it is observed that ice floats on water. Why?
Ans 18. Ice floats on the water since there is a large empty space inside the structure of ice due to which it becomes less in weight as compared to water and can float on water.
Que 19. Define boiling point.
Ans 19. The temperature at which a liquid starts boiling at the atmospheric pressure is known as its boiling point. OR the point at which the vapour pressure of the liquid becomes equal to atmospheric pressure.
Que 20. Why should we wear cotton clothes during summer?
Ans 20. We perspire more during summer. Cotton is a good absorber of water. It absorbs sweat and exposes it for easy evaporation. As a result, the body feels cool and comfortable. So, we should wear cotton clothes during summer.
Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Question Answer
Que 21. Why do gold, silver and platinum occur in a free state?
Ans 21. Gold, Silver and Platinum exist in a free state because metals like platinum, gold and silver are noble metals. They do not readily mix with impurities such as silica, potassium etc. And even if they do mix, we can easily separate them by adding an acid to them. Hence, these metals are present in a free state.
Que 22. Why do the gases exert more pressure on the walls of the container than the solids?
Ans 22. In gases, the particles move randomly at high speed and they collide with each other and with the walls of the container.
Que 23. Why does a desert cooler cool better on a hot dry day?
Ans 23. In a desert cooler, when hot air enters through the straw mates it evaporates the water at a fast rate because the rate of evaporation is faster on a hot dry day. And because of the faster evaporation rate, it cools the air more conveniently than on a dry hot day.
Que 24. Define latent heat of vaporization.
Ans 24. Latent heat of vaporization is the heat energy required to change 1 kg of a liquid to gas at atmospheric pressure at its boiling point.
Que 25. Why do people sprinkle water on the roof after a hot sunny day?
Ans 25. After a hot sunny day, people sprinkle water on the roof or open ground because the large latent heat of vaporisation of water helps to cool the surface. Water takes away the heat from the ground and gives a cooling effect.
Que 26. Convert 50 0C temperature to the kelvin scale.
Ans 26. Kelvin and Celsius are the two primary scales to measure temperature. We can get its kelvin value by adding the 273 in degree Celsius scale.
Here degree celsius value is equivalent to 50 0C.
Thus, its kelvin scale value would be 50 + 273 = 323 K.
Que 27. Why do we see water droplets on the outer surface of a glass containing ice-cold water?
Ans 27. The water vapour present in the air comes in contact with the cold surface of the glass, loses its energy and gets converted into droplets of water.
Que 28. How does the water kept in an earthen pot become cool during summer?
Ans 28. Evaporation happens through the small pores on it causing a cooling effect, in an earthen pot. Therefore, water kept in an earthen pot becomes cool during summer because of continuous evaporation.
Que 29. Define sublimation.
Ans 29. Sublimation is the change of a gaseous state directly to a solid state without going through a liquid state and vice-versa.
Que 30. Write the differences between evaporation and boiling.
Ans 30.

Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Question Answer
Que 31. Differentiate between solid, liquid and gas
Ans 31. Following are the differences between solid, liquid and gas

Que 32. Why are gases compressible but not liquids?
Ans 32. Gases are compressible because the intermolecular space is very large in gases, whereas liquids are not compressible because, in liquids, the intermolecular space is less.
Que 33. Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid.
Ans 33. Sublimation can be defined as the conversion between the solid and the gaseous phases of matter, with no intermediate liquid stage. Naphthalene balls will be having the property of sublimation because of which they directly vary from solid to the gaseous state without conversion into liquid. Hence, naphthalene balls will be vanishing with time leaving no solid.
Que 34. What is humidity?
Ans 34. The air holds water vapour, this air with water is called humid air and the phenomenon is called humidity.
Que 35. What is the tincture of iodine?
Ans 35. A solution of iodine in alcohol is known as a tincture of iodine. The solute is iodine and the solvent is alcohol.
Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Question Answer
Que 36. Why does the temperature of a substance remain constant during its melting point or boiling point?
Ans 36. The temperature of a substance remains constant at its melting and boiling points until all of the substance melts or boils because the heat supplied is continuously used up in changing the state of the substance by overcoming the forces of attraction between the particles. This heat energy absorbed without showing any rise in temperature is given the name latent heat of fusion/latent heat of vaporisation.
Que 37. A diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool. Which property of matter does this observation show?
Ans 37. It is given that a diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool. This is representing that the particles of water will be held together by weak forces of attraction between them and when any external force is applied the particles can be separated.
Que 38. What is normal atmospheric pressure?
Ans 38. The atmospheric pressure at sea level is 1 atmosphere and taken as the normal atmospheric pressure.
Que 39. A balloon when kept in sun, bursts after some time. Why?
Ans 39. The balloon has air filled in it. The balloon when kept in sun gets heated and the air inside it also gets heated. The molecules of air get energy and vibrate faster thereby exerting large force on the walls of the balloon. Due to this expansion of gases the balloon bursts.
Que 40. Why do the doctors advise to put strips of wet cloth on the forehead of a person having a high fever?
Ans 40. When a person has a fever, his body temperature becomes more than the normal body temperature. If we put strips of wet cloth on the forehead of a person suffering from high fever, the water evaporates taking heat from the body. Thus, moist strips will lower his body temperature.
Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Question Answer
[pdfjs-viewer url=”https://sciencemotive.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/Que-class-9-1.pdf” attachment_id=”4454″ viewer_width=100% viewer_height=800px fullscreen=true download=true print=true]