How to Find Oxidation Number How to Find Oxidation Number An oxidation number is a number assigned to an element that represents the number of electrons lost or gained by an atom of that element in the compound. it is the hypothetical charge. Oxidation states are represented by integers, that can be positive, negative, or zero. In some cases, the average oxidation state of an element is a fraction number. How to Find Oxidation Number There are certain rules to find the oxidation number: 1. Free, uncombined elemental atoms and homoatomic molecules always have an oxidation number of 0. For…
Author: Dr. Vikas Jasrotia
Fischer esterification Mechanism Fischer esterification Mechanism The Fischer esterification is an organic reaction used to convert a carboxylic acid and an alcohol to an ester using a strong acid catalyst. It is also known as Fischer-Speier Esterification. Fischer esterification is an example of nucleophilic acyl substitution based on the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon and the nucleophilicity of alcohol. The alcohol produced This can be done by washing the contents with two-thirds of de-ionized water. R1COOH + R2OH → R1COOR2 + H2O Carboxylic Acid Alcohol …
Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions Que 1. Analysis shows that nickel oxide has the formula 0.98 NiO. What fraction of the Nickel exists as Ni2+ and Ni3+ ions respectively? (a) 90%, 10% (b) 85%, 15% (c) 96%, 4% (d) 76%, 24% Ans 1. (c) According to the statements Formula is Ni0.98O1.00 So, the ratio of Ni:O = 98:100 So, if there are 100 atoms of oxygen then 98 atoms of Ni Let number of atoms of Ni+2 = x Then number of atoms of Ni+3 = 98–x Charge on Ni = charge…
Aldehyde Ketone and Carboxylic Acid Aldehyde Ketone and Carboxylic Acid Que 1. The IUPAC name of the compound having the molecular formula Cl3C – CH2CHO is (a) 3, 3, 3- trichloropropanal (b) 1, 1, 1- trichloropropanal (c) 2, 2, 2- trichloropropanal (d) Chloral Ans 1. (a) 3, 3, 3- trichloropropanal Que 2. The IUPAC name of CH3COCH(CH3)2 is (a) 2-methyl-3-butanone (b) 4-methylisopropyl ketone (c) 3-methyl-2-butanone (d) Isopropylmethyl ketone Ans 2. (c) 3-methyl-2-butanone Que 3. Identify compound X in the following sequence of reactions: Ans 3. (c) Reason: The following reaction takes place Que 4. In the following reaction, product P…
Electrochemistry Quiz Class 12 Chemistry The quiz Electrochemistry Quiz Class 12 Chemistry covers the whole chapter. The questions asked are important for both board examinations and various competitive examinations such as NEET, JEE, etc. Students will get exact marks along with the answers after the completion of the quiz. Electrochemistry is the study of the production of electricity from the energy released during the spontaneous chemical reaction and the use of electrical energy to bring about non-spontaneous chemical transformations. The cells used for this purpose are Electrochemical Cells and electrolytic cells. Electrochemical Cell: A cell that converts the chemical energy…
Multiple Choice Questions Redox Reaction Class 11 Multiple Choice Questions Redox Reaction Class 11 Que 1. Among NH3, HNO3, NaN3 and Mg3N2 the number of molecules having nitrogen in negative oxidation state is (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4 Ans 1. (c) Calculating the oxidation state of nitrogen in given molecules Oxidation state of N in NH3 is x + 3 × (+ 1) = 0 or x = – 3 Oxidation state on N in NaNO3 is 1 + x + 3 × (– 2) = 0 or x = + 5 Oxidation state…
Difference Between Atom and Element Difference Between Atom and Element When you are studying chemistry, terms like pure substance, elements, compounds, and atoms are the most commonly used terms amongst others. We all know that a substance is made up of elements and atoms. Atoms and elements are well known to almost all around. But did you ever think about the difference between the two? Let’s find the difference between the two. The main difference is elements are made of atoms. Other differences are given below: S. No. Element Atom 1. An element is a primary form of a substance…
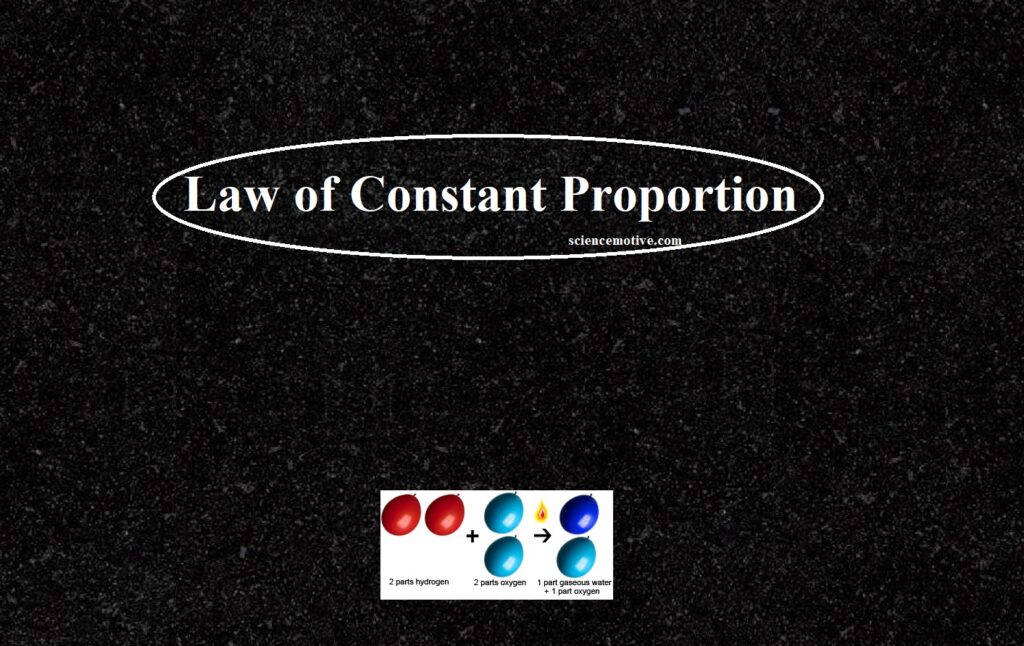
Law of Constant Proportion Law of Constant Proportion The combination of elements to form compounds is governed by the following five basic laws: Law of Conservation of Mass Law of Constant Proportion Law of Multiple Proportions Gay Lussac’s Law of Gaseous Volumes Avogadro’s Law In Chemistry, the Law of Definite Proportion is sometimes called Proust’s law or the law of constant composition. According to this law, a chemical compound always contains the same elements combine together in a fixed ratio by mass. This implies that any pure sample of a compound, no matter the source, will always consist of the same elements…
Reactivity Series of Metals Reactivity Series of Metals The metal reactivity series is a very important concept in chemistry, placing the metals, in order of reactivity from most reactive to least reactive. It’s also a useful method in predicting the products of simple displacement reactions involving two different metals, as well as it also provides an insight into why different metals are extracted from their ores in different manners. The reactivity of metals is because of their incomplete outer orbitals or due to their electronic configuration. Metals form positively charged ions as they tend to lose electrons. Metals with high…
Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Thermodynamics (Greek word thermo means heat and dynamics means motion) is the branch of science which deals with the study of different forms of energy and the quantitative relationships between them. The study of thermodynamics is purely based upon three generalizations these are first, the second, and third law of thermodynamics. Some important definitions involved: System: A system is the part of the universe that is under observation or investigation. Surroundings: The part of the universe except the system is called surroundings. The system and surroundings are separated by a boundary…